Av Rolf Theil
How the language evolved
Many related languages across Europe are called Romani. To separate them, we call them Norwegian-Romani, Swedish-Romani, Finnish-Romani, English-Romani, Welsh-Romani and so on. We use Romani as a generic term for the entire language group.
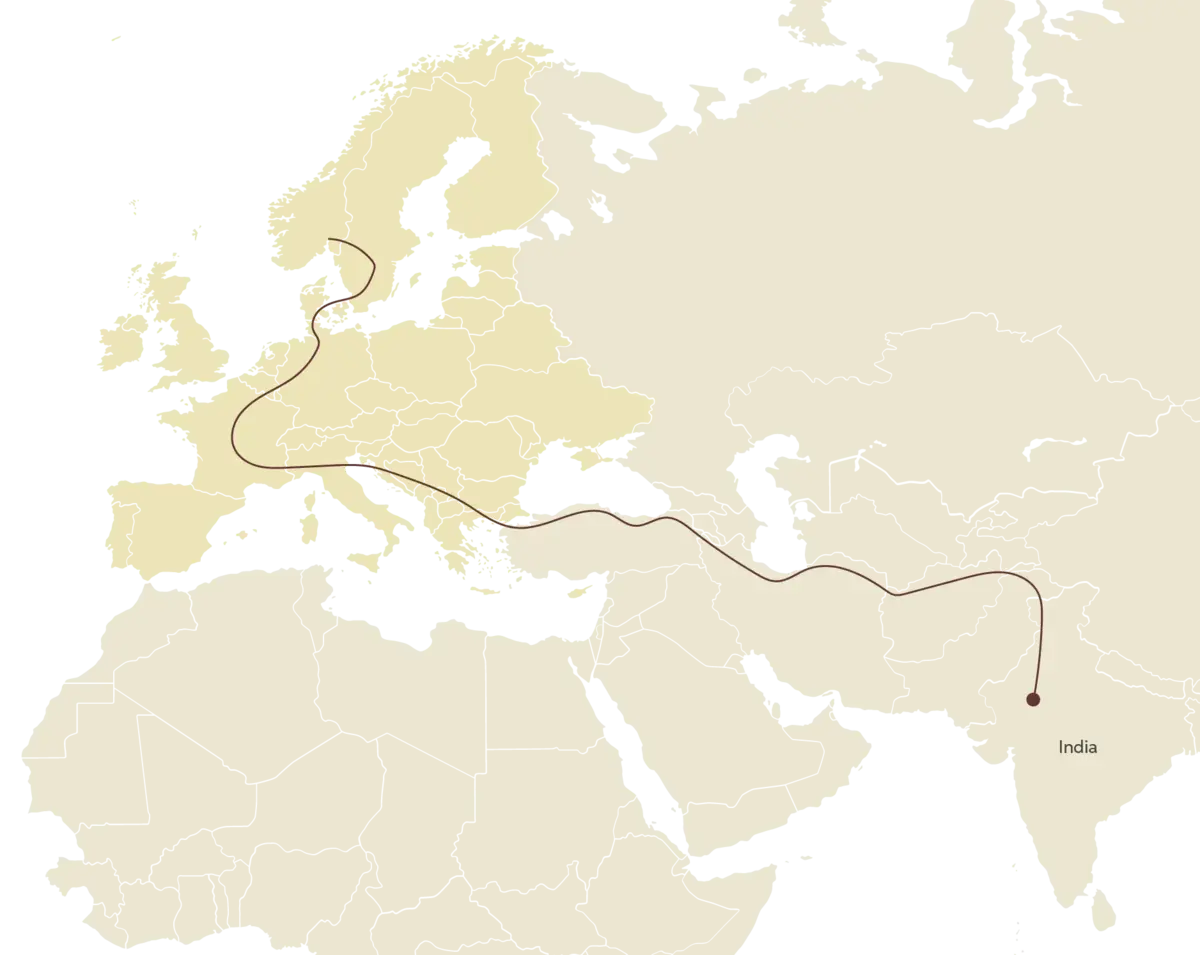
People who spoke Romani went to the Balkans from Asia Minor in the mid-thirteenth century. Their language clearly shows that they originally came from the northern parts of the Indian subcontinent. About 60% of the words and most of the grammatical structures in traditional Romani languages originate from Indo-Aryan languages. Indo-Aryan languages are spoken mainly in Pakistan, Nepal, northern India and Bangladesh. Examples of Indo-Aryan languages include Punjabi, Gujarati, Hindi, Urdu, Nepali and Bengali.
See the language's migration route on the map below: